Welcome back to another adventure along The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Medicine! My name is Arunima, and today I’d like to introduce you to the first installment of a new branch of the Guide—Biomedical Engineering (BME).
We live in a time where technology doesn’t just sit on our desks or in our pockets—it’s woven directly into our bodies and our healthcare. From prosthetic limbs that move with thought, to artificial organs, to nanorobots that one day may repair cells, BME is the space where innovation meets human life. This series—BME x Medicine—will explore how engineers and scientists work together to design solutions that don’t just treat disease, but often restore what it means to be human.
But what do I mean by Biomedical Engineering? Let’s define it.
Biomedical Engineering (BME) is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology. It’s about building bridges between two worlds: the precision of engineering and the complexity of the human body.
At first glance, medicine and engineering might seem far apart: one focused on healing, the other on building. But both are rooted in problem-solving—asking “What’s broken?” and “How can we fix it?” The more I’ve studied, the more I’ve realized the divide isn’t as wide as it seems. The human body itself is already a marvel of engineering: bioelectric currents racing through our neurons, precisely crafted extracellular matrices giving tissues their strength, and intricate feedback systems designed to keep us functioning every second of the day. Biomedical Engineering takes inspiration from these natural designs, borrowing their elegance and precision to imagine new ways of enhancing human life.
As someone fascinated by both human physiology and technological design, I’ve spent time studying how medical devices, imaging systems, and computational models have the potential to shape patient care. What I’ve found is that BME is more than just gadgets—it’s about reimagining healthcare itself. In this series, we’ll explore topics like:
- Prosthetics & Neural Interfaces – how machines connect to mind and muscle
- Medical Imaging – from MRI to AI-powered diagnostics
- Biomaterials & Tissue Engineering – designing scaffolds and organs from scratch, and bioprinting using natural and synthethic substances
- Nanotechnology in Medicine – therapies at the molecular scale
- Ethics & Accessibility – who gets access to tomorrow’s tech, and at what cost?
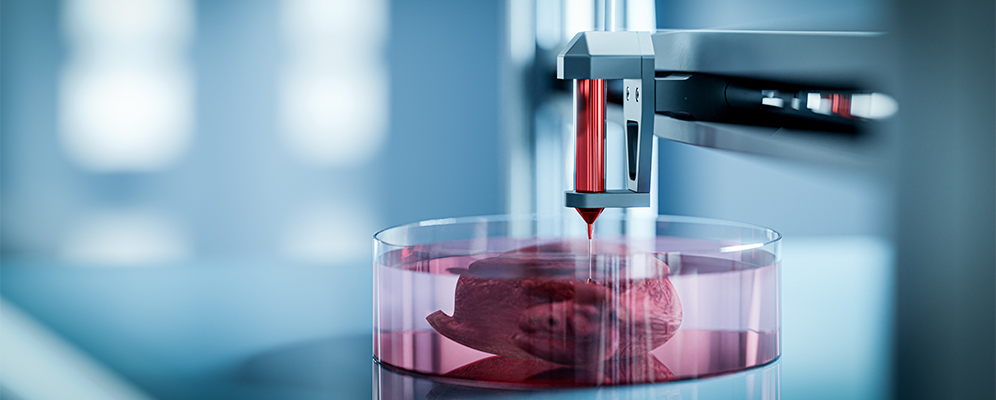

Personally, I’m especially drawn to scaffold designs and nanotissue engineering—areas that sit at the frontier of regenerative medicine. The idea that we can guide cells to grow into functioning tissues, or even entire organs, through carefully engineered structures is mind-blowing to me. Nanotissue engineering, in particular, feels like peering into the future of medicine: working at the molecular level to create tissues that mimic the elegance and complexity of nature itself. These interests aren’t just abstract—they’re what inspire me to explore how engineering can help solve shortages in organ transplants, accelerate wound healing, and push us closer to therapies that truly restore and prevent rather than just replace and medicate.
My goal here is to show how Biomedical Engineering makes the future of medicine tangible. Each post will peel back the layers of complexity without stripping away the wonder. Whether you’re a med student, an aspiring engineer, or just curious about how science reshapes healthcare, I invite you to join me on this journey. Stay tuned to The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Medicine as we uncover the marvels and milestones of Biomedical Engineering. Until then, keep exploring—and stay curious!

Leave a comment