Welcome back to another adventure along The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Medicine! Today, we will cover a recent study that highlights the use of Stem Cell Therapy to help treat Type 1 Diabetes!
In a landmark case study, researchers have successfully reversed type 1 diabetes using stem cell therapy. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to the loss of insulin production. Insulin is essential for regulating blood sugar levels, and without it, individuals must rely on lifelong insulin therapy. This new approach aims to restore natural insulin production through stem cell technology.
The therapy revolves around differentiating stem cells into insulin-producing beta cells. These cells are then transplanted into the patient’s body. The key advancement here is the development of a process that generates beta cells closely mimicking those found in the pancreas. These lab-grown cells can respond to blood glucose levels and secrete insulin accordingly.
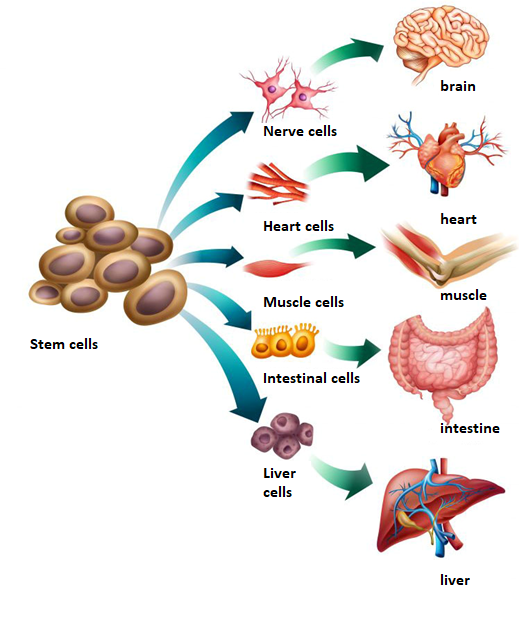
To ensure the success of the transplantation, researchers also focused on creating an environment where the transplanted cells could thrive and evade immune attack. By addressing these two major challenges—immune rejection and beta cell functionality—scientists achieved significant progress.
In the reported case, the patient experienced a dramatic improvement in blood sugar levels after receiving the stem cell treatment. This marks a crucial step in the pursuit of a functional cure for type 1 diabetes. While insulin therapy manages symptoms, stem cell therapy offers the potential for long-term remission or reversal of the disease.
However, this treatment is still in the early stages, with further research needed to confirm the long-term efficacy and safety. The therapy also requires a careful balance to prevent immune rejection without compromising the patient’s overall immune function. If successful, it could significantly reduce or eliminate the need for daily insulin injections for millions of people worldwide.
The success of this therapy highlights the potential of regenerative medicine to transform how we treat autoimmune diseases. For type 1 diabetes patients, this could mean a future where insulin injections and blood sugar monitoring become things of the past. This case study also opens doors to further exploration of how stem cells can be used to combat other autoimmune and chronic diseases.
Continued research will aim to refine the process, improve cell survival rates, and enhance immune compatibility. Scientists are also working on making the therapy more accessible and scalable, ensuring that it benefits a larger population.
This case study is a significant milestone in diabetes research and regenerative medicine. While there is still a long way to go before this therapy becomes widely available, it represents hope for a more effective and permanent solution for type 1 diabetes. Stay tuned to “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Medicine” as we uncover more marvels and milestones in the field of medical science. Until then, keep exploring, and stay curious!

Leave a comment