Welcome back to another adventure along The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Medicine! Today, we will discuss the relationship between time-restricted eating, a recent fad, and improved blood sugar levels and fat loss.
In recent years, various forms of intermittent fasting, such as time-restricted eating (TRE), have gained popularity for their potential health benefits. According to a recent study, a growing body of evidence supports the idea that TRE could play a key role in improving blood sugar control and promoting fat loss, especially in individuals at risk for metabolic disorders.
But how exactly does time-restricted eating work? In this method, individuals eat all their daily calories within a specific window of time, typically ranging from 6 to 10 hours, while fasting for the remainder of the day. Unlike traditional diets that focus on what to eat, TRE emphasizes when to eat, aligning food intake with the body’s natural circadian rhythms. This approach capitalizes on the body’s internal clock, which regulates metabolic processes such as insulin sensitivity, digestion, and fat storage.
One of the most compelling findings highlighted in the study is TRE’s impact on blood sugar control. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar by helping cells absorb glucose. Over time, poor insulin sensitivity—often a result of a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, or a high-calorie diet—can lead to type 2 diabetes.
Studies have shown that individuals who adopt TRE experience improved insulin sensitivity and reduced blood glucose levels. In particular, the study emphasizes research indicating that people who confine their eating to an early window in the day (for example, from 8 a.m. to 4 p.m.) show enhanced glucose tolerance compared to those who eat over a longer period. This supports the idea that our bodies are better equipped to handle food during daylight hours, aligning with the natural rise and fall of insulin levels.
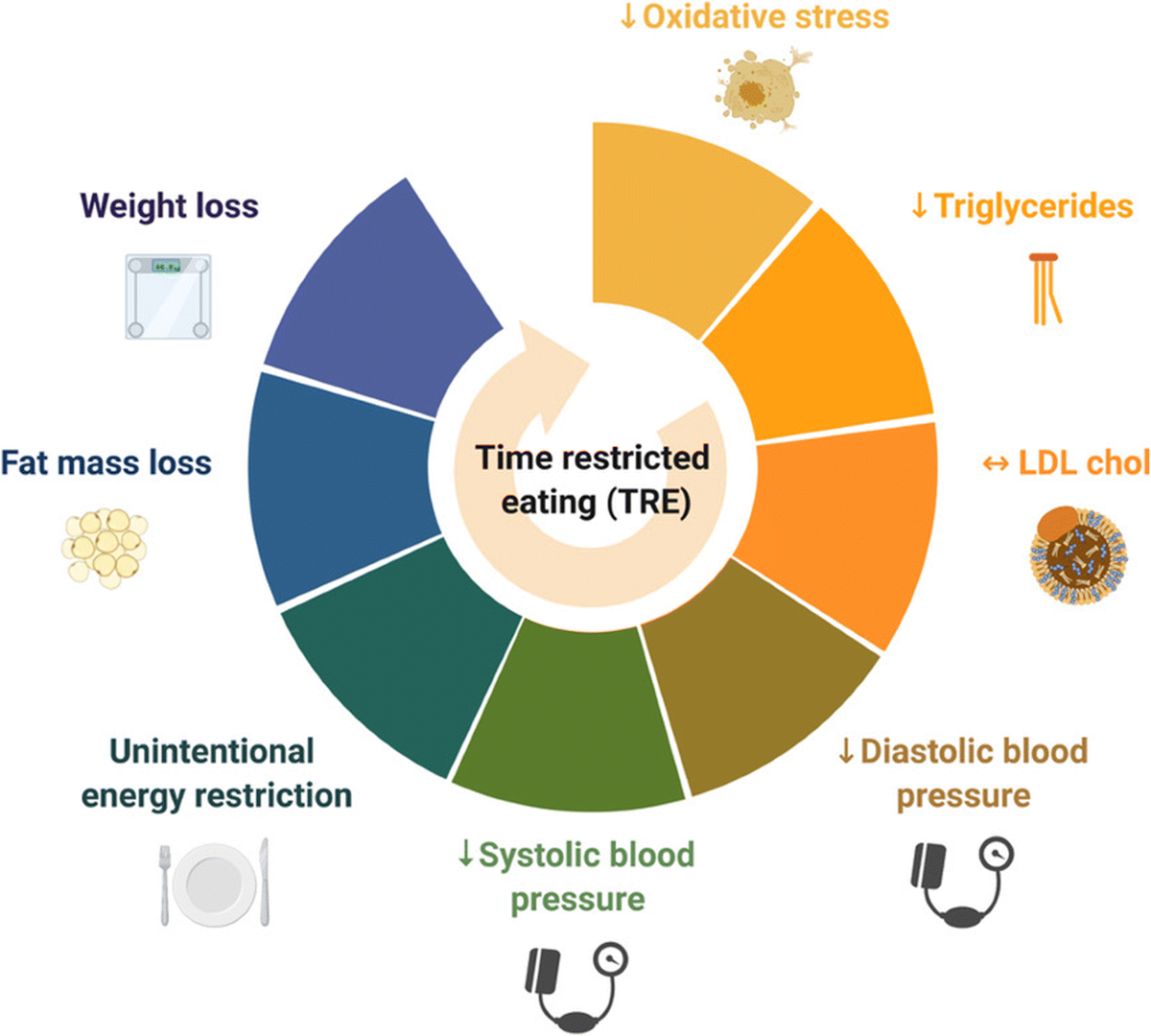
Another exciting potential benefit of TRE is its effect on fat loss. The study notes that by restricting the eating window, people naturally consume fewer calories, which may lead to weight loss. However, it’s not just the calorie reduction that matters. During the fasting period, the body shifts its energy source from glucose to stored fat, which can promote fat burning. This process, known as lipolysis, helps in reducing body fat, particularly the visceral fat that accumulates around internal organs and is associated with higher risks of cardiovascular disease.
A study mentioned by researchers found that participants practicing TRE showed significant reductions in fat mass, without the loss of lean muscle. This makes TRE an attractive option for people looking to improve body composition while maintaining muscle mass, an important factor for long-term health and metabolism.
While the study primarily focuses on the metabolic benefits, TRE’s advantages extend beyond blood sugar control and fat loss. Research suggests that time-restricted eating may also help reduce inflammation, improve cardiovascular health, and potentially enhance longevity by promoting cellular repair processes like autophagy, where the body removes damaged cells.
If you’re thinking about incorporating TRE into your lifestyle, the good news is that it’s flexible and customizable. The most common form is the 16:8 method, where people fast for 16 hours and eat within an 8-hour window. For beginners, starting with a 12-hour eating window and gradually reducing it can ease the transition.
It’s also important to prioritize nutrient-dense foods during the eating window. While TRE can lead to calorie reduction, the quality of those calories matters. Opt for whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables to maximize the health benefits.
Time-restricted eating is not just another diet fad. As the study suggests, it’s a lifestyle approach that taps into the body’s natural rhythms to improve metabolic health. By optimizing insulin sensitivity, promoting fat loss, and supporting overall well-being, TRE holds promise for individuals looking to make sustainable changes to their health. Stay tuned to “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Medicine” as we uncover more marvels and milestones in the field of medical science. Until then, keep exploring, and stay curious!


Leave a comment